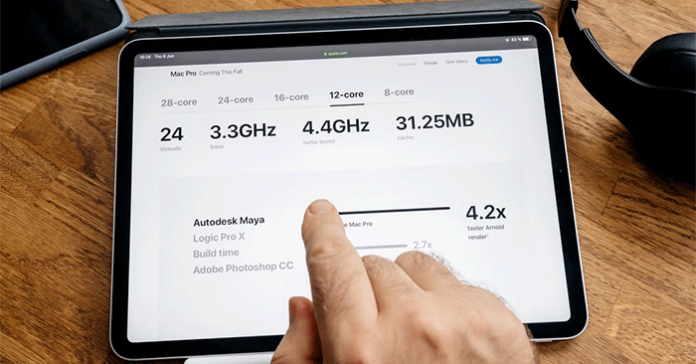
Choosing the right CPU involves understanding two key factors: Core count and clock speed. Each factor plays a distinct role in computer performance, but should you buy a CPU with more cores or a higher clock speed?
What is a CPU core? What is CPU clock speed?
When choosing a CPU, you need to compare different specifications to find the one that best suits your needs. The two most important specifications you need to know are the number of cores and the CPU clock speed.
- CPU core: A core is an individual processing unit within a CPU. Modern CPUs can have multiple cores, typically ranging from 2 cores in basic models to 12 cores in higher-end CPUs. Each core can handle its own tasks, allowing for multitasking and parallel processing.
- Clock speed: Measured in gigahertz (GHz), clock speed indicates the number of cycles a CPU core completes per second. Higher clock speeds mean each core can process tasks faster, improving performance in tasks that rely on single-threaded execution.
In terms of value, both are extremely important, but which spec should you prioritize?
When should more CPU cores be preferred?

Higher core counts are beneficial for situations where multiple tasks run concurrently or applications designed to use multiple threads. Consider the following:
- Multitasking: Running multiple applications at the same time, such as web browsers, music players, gaming, and live streaming, can overload the single-core processor. Multi-core CPUs distribute these tasks across multiple cores, ensuring smoother performance.
- Multi-threaded application: Video editing tools, 3D rendering, and virtualization software are optimized for efficient use of multiple CPU cores. For example, video editing software can assign different cores to handle rendering, encoding, and multiple background processes simultaneously.
So, when running multiple programs, you need more cores.
When is a high CPU clock speed better?

Tasks that depend on the speed of each core will benefit more from higher clock speeds. For example:
- Play games: Many games are designed to run on one or two cores. Higher clock speeds ensure these games run smoothly, as each core processes game data faster.
- Single-threaded application: Old software and some modern applications are not optimized for multiple cores. For these programs, a faster clock speed improves performance more than additional cores.
When it comes to gaming, higher clock speeds really matter.
Balance between cores and clock speeds
Most applications today benefit from multi-core CPUs with high clock speeds. But if you want the best performance on a tight budget, you'll have to find a CPU that balances core count and clock speed for your specific needs.
- General use: For everyday tasks like web browsing, streaming, and document editing, a CPU with a moderate number of cores (4 to 8) and a good clock speed (about 3.0 GHz) is enough.
- Professional workload: If you engage in video editing, 3D modeling, or software development, choose a CPU with a higher core count (8 cores/16 threads or more) and competitive clock speeds to efficiently handle applications demanding applications.
- Play games: Older games typically use one or two threads (one CPU core), while modern AAA titles use up to four to six threads (two or three CPU cores). Therefore, gamers should prioritize higher clock speeds (3.5GHz or higher) and enough CPU cores (at least 4 cores/8 threads) to ensure optimal performance in modern games.
There's no one-size-fits-all answer when choosing a CPU (at least when you're on a tight budget). So before buying a CPU, evaluate the applications you'll be running and try to find a CPU that balances core count and clock speed based on your intended use case.